But they are useless. They can only give you answers”
Pablo Picasso, On Computers
Over the past few years, we’ve witnessed remarkable advancements in AI technologies that are reshaping industries, automating tasks, and augmenting human capabilities but before we proceed to take a look at how technology would impact jobs of future, let’s take a trip back to 1800s and see how jobs were impacted when steam powered machines were introduced in the factories.
Rise of Luddites:
In the early 1800s the town of Nottinghamshire found itself at the epicenter of a technological revolution that would forever change the textile industry. Steam-powered mechanical frames had arrived, threatening to render the labor of skilled artisans obsolete. These artisans, possessing highly specialized and finely honed skills, suddenly found themselves in a world that no longer had a place for their craftsmanship.
Faced with the impending loss of their livelihoods and the erosion of their once-prized skills, a group of indigent laborers banded together in secret societies, rallying under the banner of a fictional character named Ned Ludd—a figure reminiscent of Robin Hood but updated for the industrial age. These defiant individuals proudly donned the title of “Luddites.”
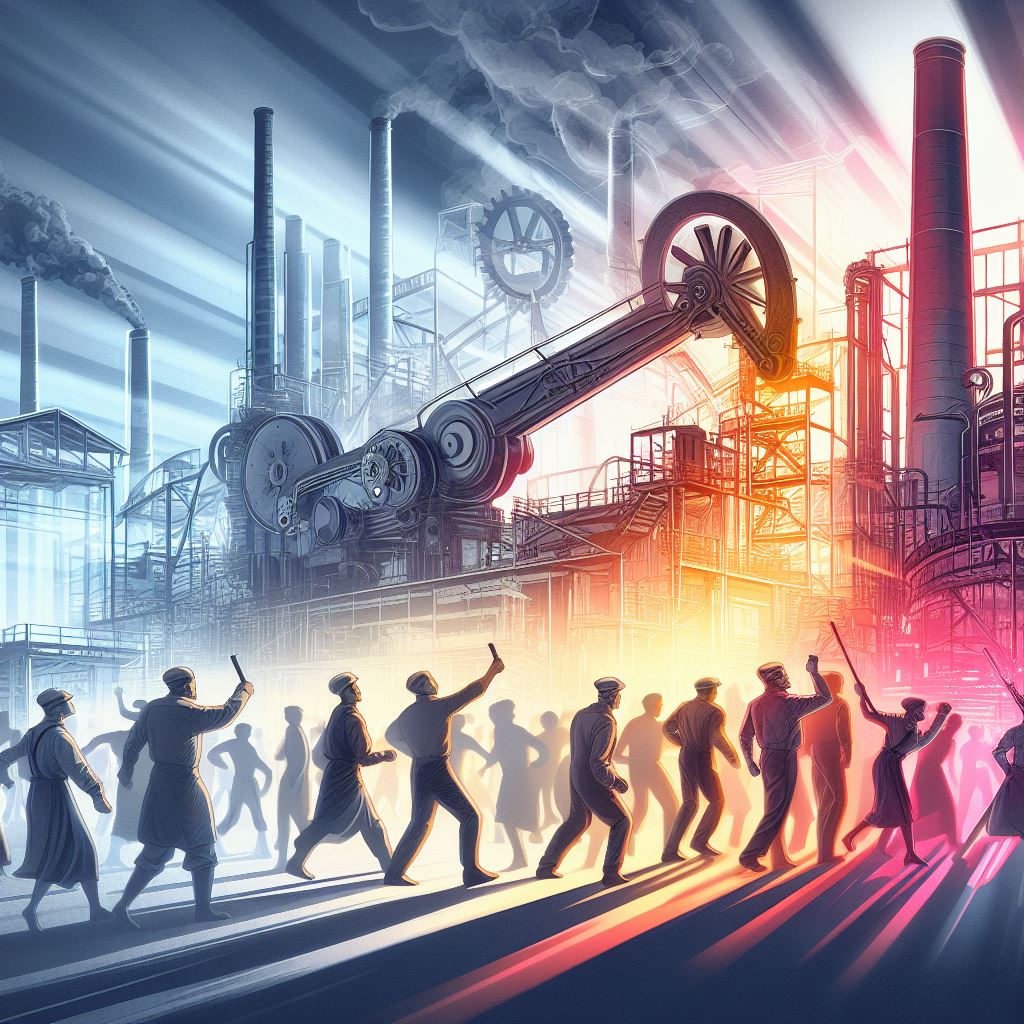

Luddites stormed hosiery factories, their sledgehammers in hand, and ruthlessly smashed the owners’ new and disruptive machines. This bold uprising quickly rippled across neighboring communities, sparking a movement that was so severe that more more British soldiers were battling the Luddites than were deployed against the French in the Iberian peninsula.
Shift in the Job Market
As the Luddites protested the initial wave of job losses, the adoption of steam-powered machines in various industries brought about a significant shift in the job market and the dynamics of human-machine collaboration. Let us walk through and take a look at the impact machines bought in the work culture.
1. Transition from Craftsmanship to Factory Labor:
- Prior to the invention of steam powered machines, many businesses relied on experienced craftsmen and artisans who made products by hand. Though the machines made manual skill less necessary displaced some skilled artisans initially, however they also introduced many new jobs in the market. Factories required workers to operate and maintain these machines, leading to a surge in demand for factory workers, machine operators, and mechanics thus factory work grew more common as a result.

2. Urbanization and Migration:
- The rise of factories and industrial centers led to individuals moving from rural regions to urban centers in pursuit of employment opportunities. The influx of people reshaped demographics and created a need for urban infrastructure and services including sewage, water supply, public transit, and healthcare. Thus, more staff was hired to facilitate this growing demand.

4. Specialization and Division of Labor:
- As production processes became more mechanized, jobs became more specialized. Within the manufacturing line, workers were given specific tasks to perform, which led to the division of labor. While efficiency grew, the demand for skilled craftsmen decreased as a result of specialization.
5. Impact on Agriculture:
- Due to the migration of people to urban centers Agricultural workforce diminished, this further contributed to increased mechanization in agriculture.
6. Growth of Support Industries:
- In order to support the machinery and factories, sectors including steel production, coal mining, and transportation expanded, which significantly increased the number of jobs in connected fields. This includes positions in logistics, infrastructure construction, and mining.
7. Expansion of White-Collar Jobs:
- In order to support the growing demand for machines, sectors including steel production, coal mining, and transportation expanded, which saw significant increase in White-Collar jobs in fields such as logistics, infrastructure construction, and mining.
8. Changes in Working Conditions:
- Higher production speeds and efficiency came at the cost of degrading working conditions. Workers were made to work for long hours with poor safety standards. This further led to rise of labor movements and unions emerged to advocate for workers’ rights and improved conditions.
9. Technological Advancements and Training:
- As steam powered machines took center stage, the demand for skilled workers who could operate and maintain them led to the formation of technical schools and vocational training programs.
In summary, Steam powered machines fueled economic growth and innovation, leading to the creation of new products, services, and markets which gave rise to entirely new industries and job categories. While it displaced some traditional jobs, it also created new opportunities, changed the nature of work, and contributed to significant economic and societal changes during the Industrial Revolution.
If you found this article insightful and would like to stay updated on content like this in future, then please follow our WhatsApp channel.

